EVAP Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor Test — Step-by-Step DIY for P0452–P0453
Tools: Scan tool (or multimeter), back-probe leads
Difficulty: 2/5 Time: 15–25 minutes
Last Updated: October 2025
Common Symptoms of a Bad FTP Sensor
- Check Engine Light with P0452, P0453, or P0454
- Hard start or long crank after refueling
- EVAP readiness monitor not completing
- Incorrect or unstable pressure readings on scan tool
- Strong fuel smell or rough idle during EVAP purge
Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor Operation
The Fuel Tank Pressure (FTP) sensor monitors the pressure or vacuum in the EVAP system. It is a 3-wire sensor that includes a 5-volt reference, ground, and signal circuit.
As system pressure changes, the sensor outputs a corresponding voltage to the engine control module (ECM), allowing it to detect leaks and verify EVAP component operation.
Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor Test
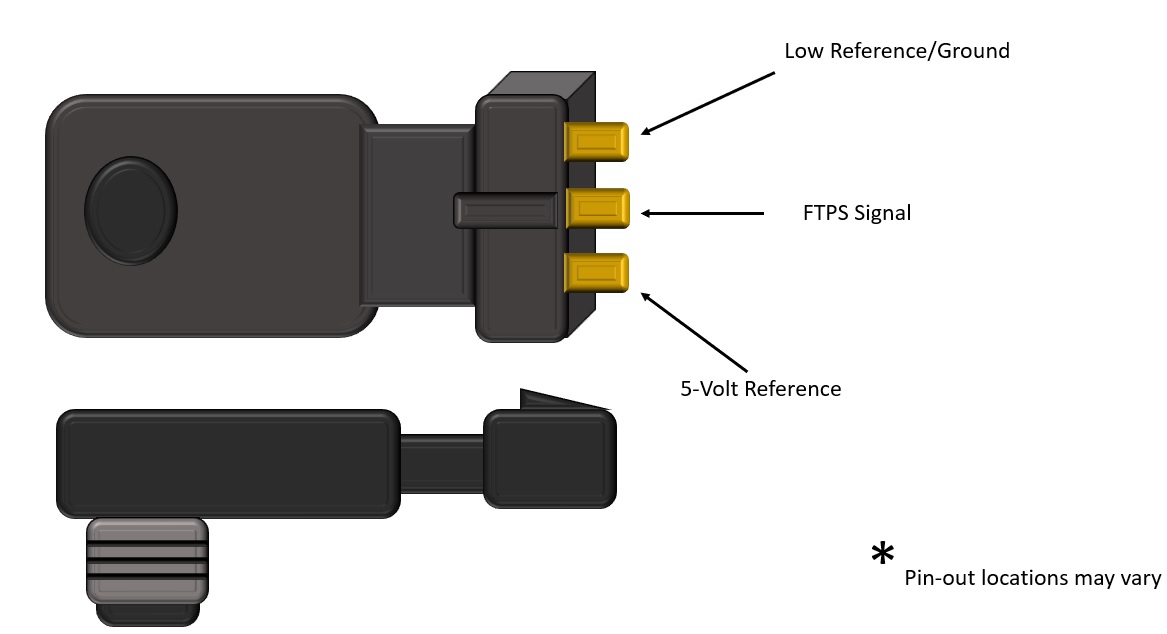
1. Check Sensor Inputs
- Unplug sensor connector.
- Turn the key ON (engine off).
- Verify 5-volt reference and ground on the correct pins using a multimeter.
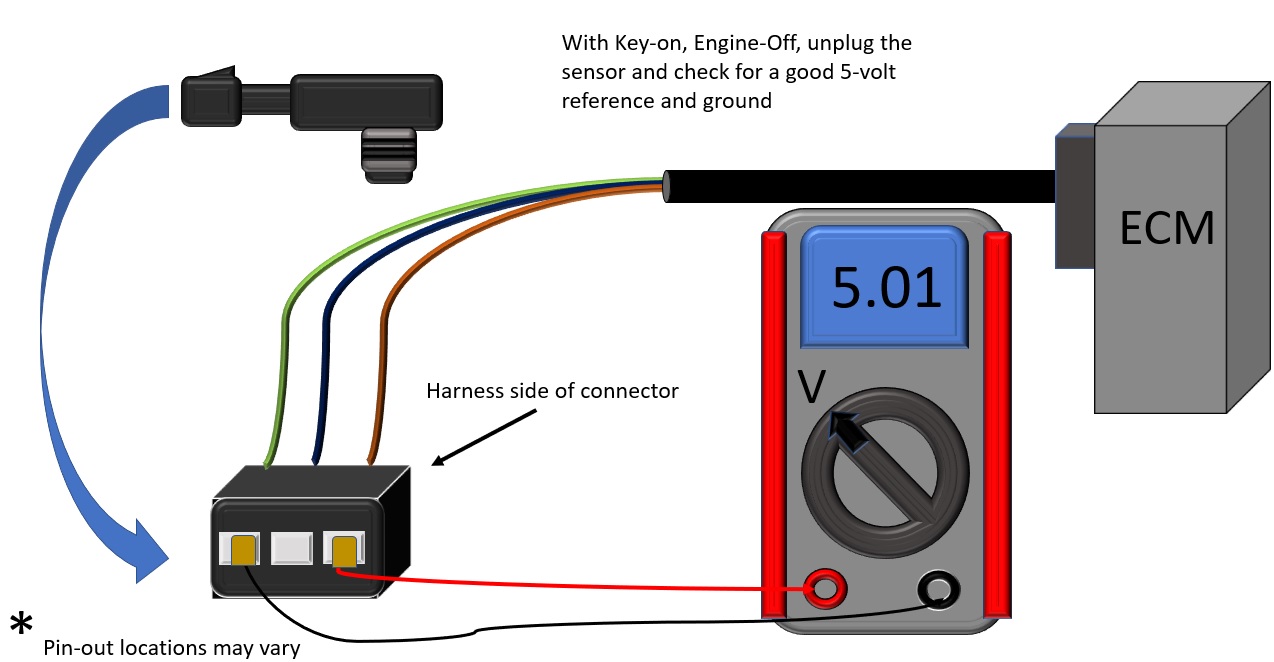
Tip: Check service information or contact GoTech Techline for pinout details.
2. Check Sensor Output
- Reconnect sensor.
- With key ON, engine OFF, read FTP voltage on a scan tool. (See table below for normal ranges.)
Tip: Use back-probe leads so you can read the signal wire without damaging the connector.
- Without a scan tool, back-probe the signal wire and check voltage using a multimeter.
- While monitoring, activate the purge solenoid via scan tool or jumper wire.
- Look for a small voltage change (~50–500 mV). This confirms the sensor responds to pressure changes and isn’t stuck.
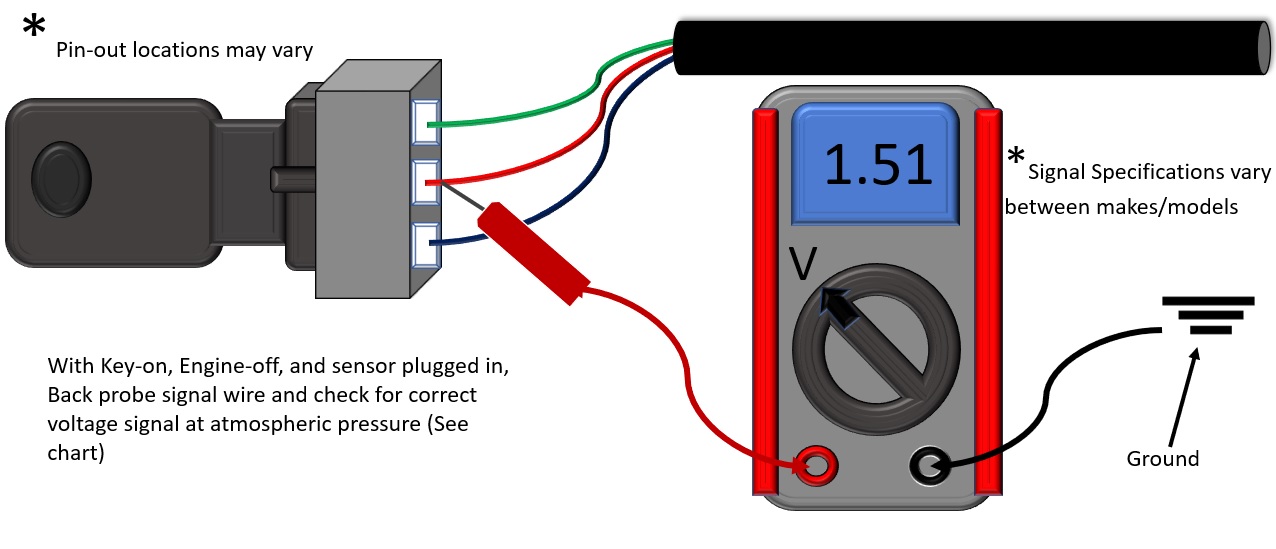
Tip: Some systems maintain slight pressure or vacuum. Remove the gas cap to equalize before testing.
FTP Voltage Reference Table by Make
| Make | Typical FTP Voltage (Atmospheric) |
|---|---|
| GM | ~1.5 V (rises with vacuum) |
| Toyota/Lexus | ~3.3 V |
| Honda/Ford | ~2.5 V |
| Nissan/Infiniti | 3.3–4.2 V |
| Hyundai/Kia | ~2.5–3.0 V |
Vehicles This Applies To
GM, Ford, Toyota/Lexus, Honda/Acura, Nissan/Infiniti, Hyundai/Kia, and most OBD-II vehicles with EVAP monitoring systems.
